Trading the FTSE 100: A Comprehensive Guide

6 minutes for reading
On 30 November 2023, we analysed the intricacies of the FTSE 100 index, exploring its structural components and trading strategies. As the premier stock index in the UK, the FTSE 100 reflects fluctuations in the stock prices of the 100 largest companies traded on the London Stock Exchange.
Understanding FTSE 100 for beginners
The Financial Times Stock Exchange Index 100 (FTSE 100), known as "Footsie" in trading circles, is one of the leading stock indices in Europe. The FTSE Group calculates its value from the stock prices of the foremost 100 companies in the UK, whose securities are actively traded on the London Stock Exchange (LSE).
The companies included in the FTSE 100 account for approximately 80% of the total LSE capitalisation. The index composition is reviewed quarterly, with more substantial companies in terms of market capitalisation, liquidity, and profitability replacing the weaker ones.
Distribution of companies in the FTSE 100 by sectors
- Consumer goods and services - 30%
- Finance - 25%
- Engineering - 20%
- Mining - 10%
- Telecommunication - 5%
- Healthcare - 5%
- Oil and gas - 4%
Historical performance of the FTSE 100
The first calculation of the FTSE 100 was done in 1984, with an initial benchmark value of 1,000 points. At the time of writing, the index has demonstrated stable growth, although corrections were noticeable during the economic crises of 2008-2009 and 2020. The maximum value of the FTSE 100 was reached in February 2023 at 8,047 points. Currently, the index is around 7,420 points.
FTSE 100 Index chart, 1989–2023*
How does the FTSE 100 index work?
For inclusion in the FTSE 100, a company must meet specific criteria set by the FTSE Group. For example, the index is calculated based on the market capitalisation of companies: the higher the company's performance, the greater the weight the company has in the index basket, and the stronger the impact on its movements.
Top 10 companies influencing the FTSE 100
- Royal Dutch Shell plc (LSE: SHEL)
- AstraZeneca PLC (LSE: AZN)
- HSBC Holdings PLC (LSE: HSBA)
- Unilever PLC (LSE: ULVR)
- BP PLC (LSE: BP)
- Diageo PLC (LSE: DGE)
- Rio Tinto PLC (LSE: RIO)
- GSK PLC (LSE: GSK)
- Glencore PLC (LSE: GLEN)
- British American Tobacco PLC (LSE: BATS)
If the shares of these companies grow, FTSE 100 quotes generally tend to move upwards, and vice versa: a decrease in their stock prices might lead to a reduction in the index.
Factors influencing the FTSE 100
- Global stock market conditions. If global markets show overall positive dynamics, then the FTSE 100 has favourable conditions for potential growth, and vice versa
- Important political and economic events in the UK. Developments such as Brexit could cause significant market fluctuations and impact the FTSE 100
- Speeches and comments from top officials in the UK. Statements and comments from high-ranking officials can trigger market reactions that can influence the index
- Quarterly and annual corporate reports. These are especially relevant for large companies whose securities are included in the index basket
- Commodity price indices. It mainly concerns companies from the FTSE 100 whose stock prices depend on commodity prices
What are the other FTSE indices?
- FTSE 250 is an index of medium-capitalisation companies, including the next-largest 250 companies after the FTSE 100
- FTSE 350 represents a combination of the FTSE 100 and FTSE 250 indices
- FTSE SmallCap is an index of companies with small capitalisation listed on the primary market of the LSE
- FTSE All-Share is an index that includes stocks of more than 1,000 companies traded on the London Stock Exchange. It is a combination of companies from three indices: FTSE 250, FTSE 100, and FTSE SmallCap
- FTSE AIM UK50 is comprised of the 50 largest British companies by market capitalisation listed on the Alternative Investment Market (AIM)
- FTSE AIM 100 is a capitalisation-averaged index that includes the top 100 companies on the AIM
- FTSE AIM All-Share is a stock index comprised of all the companies quoted on the Alternative Investment Market that meet the liquidity and free flow requirements
Risks of trading the FTSE 100
Even though stock indices usually demonstrate growth in the long run, trading the FTSE 100 index entail certain risks. For example, an economic crisis accompanied by a deep and lengthy recession might crash stock prices and the index for a long time. At the beginning of the 1970s, the crisis seriously hurt the FTSE All-Share. Investors who put their money in the UK shares had to wait until 1982 to regain their real investments, with inflation accounted for.
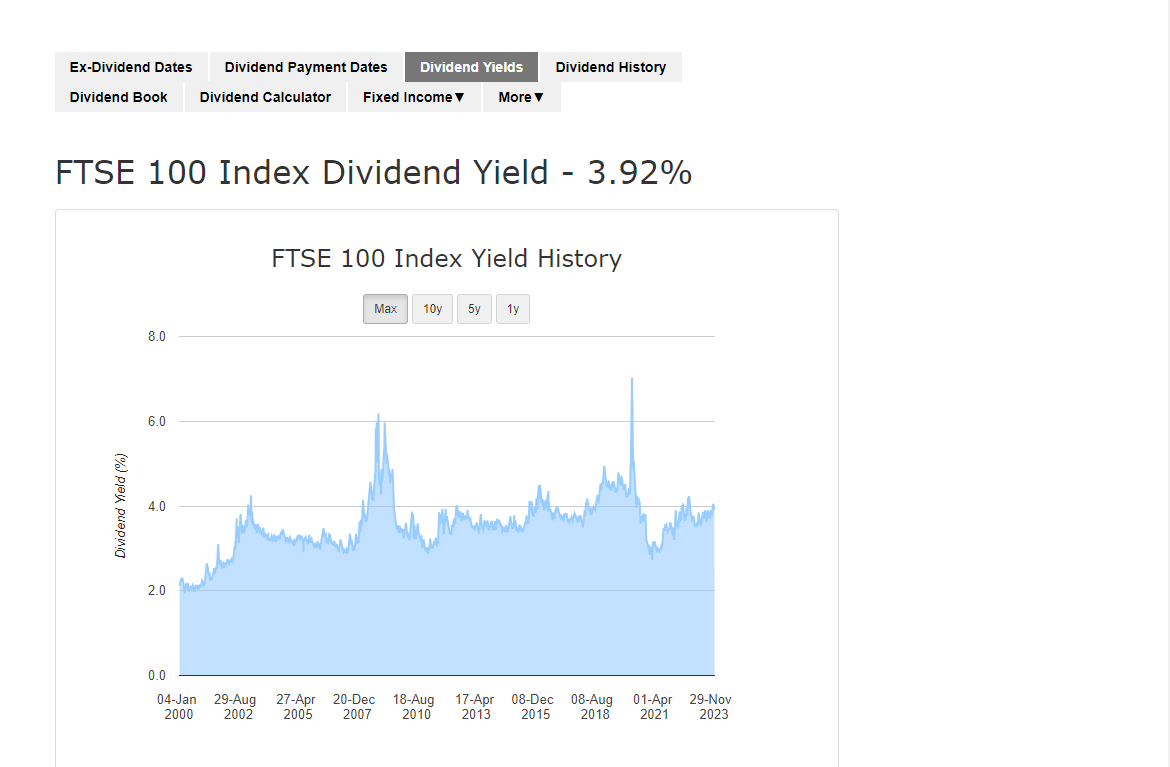
Dividends from FTSE 100 investments
Companies included in the FTSE 100 index pay dividends to their investors. According to Dividend Data, from January 2000 through November 2023, the average annual dividend yield from investments in the FTSE 100 companies ranged from 2% to 4.5%. The current annual dividend yield in November 2023 amounts to 3.92%.
How to trade the FTSE 100
- Select the financial instrument for trading or investing - ETFs, CFDs, shares, futures, or options.
- Choose a reliable broker with whom you will trade your instruments.
- Select a trading platform or a Web terminal.
- Open and deposit a trading account.
- Start trading or investing.
1. What is the FTSE 100, and why is it significant for traders?
The FTSE 100 is a popular index representing the UK's largest 100 companies, offering numerous trading opportunities due to its dynamic price movements.
2. How can one trade the FTSE 100 directly?
Trading the FTSE 100 directly involves using CFDs to speculate on the price movements of the underlying asset without owning the actual assets.
3. What is CFD trading, and how is it related to FTSE 100 trading?
CFD trading involves speculating on asset price movements like those in the FTSE 100 without acquiring the underlying assets.
4. How does trading FTSE 100 ETFs work?
Trading FTSE 100 ETFs involves taking a position on the ETF's price, calculated using the fund's net asset value through CFD trading without owning the underlying asset.
5. What are the advantages of trading FTSE 100 shares?
Trading FTSE 100 shares allows you to target specific stocks within the index without exposure to the entire index, using CFDs to go "long" or "short" based on price prediction.
6. How can a trader manage the risks associated with CFD trading in the FTSE 100?
Managing risks in CFD trading can involve setting stop-loss limits, monitoring market trends, and using a risk management strategy to avoid substantial losses.
7. What are the general trading hours of the FTSE 100?
The FTSE 100 typically trades from 4 pm to 12.30 am Monday to Thursday and 4 pm Friday to 12.30 am Saturday (UTC+8).
8. What role does economic news play in FTSE 100 trading strategies?
Economic news can induce volatility in the market, influencing the prices of the FTSE 100 constituents and thereby affecting trading strategies.
* – Past performance is not a reliable indicator of future results or future performance.
The material presented and the information contained herein is for information purposes only and in no way should be considered as the provision of investment advice for the purposes of Investment Firms Law 87(I)/2017 of the Republic of Cyprus or any other form of personal advice or recommendation, which relates to certain types of transactions with certain types of financial instruments.
The stock charts in this article are provided by the TradingView platform, which offers a wide range of tools for analysing the financial markets. It is a convenient, high-tech online market data charting service that allows users to perform technical analysis, research financial data, and communicate with other traders and investors.










 are complex instruments and come with a high
are complex instruments and come with a high  of losing
of losing  rapidly due to
rapidly due to  . 65.68% of retail investor accounts lose
. 65.68% of retail investor accounts lose  when trading
when trading  with this provider. You should consider whether you understand how CFDs work and whether you can afford to take the high
with this provider. You should consider whether you understand how CFDs work and whether you can afford to take the high